The insurance sector has traditionally been associated with conservatism, intricacies, and reliance on intermediaries and manual practices. InsurTech startups have begun dismantling this status quo by designing digital-first platforms that create simple, timely, and transparent insurance experiences for customers and partners.
Friendly capital and modern engineering have completely transformed Traditional Insurance Models by streamlining the creation of modular software, APIs, automation, and analytics. By working with an Insurance software development company, these startups can turn ideas into scalable products in a couple of months and continually address the friction points that have kept policyholders and agents from experiencing them for decades.
What is InsurTech?
InsurTech (insurance + technology) refers to technology-driven businesses and solutions that disrupt the insurance value chain across product design, distribution, underwriting, claims, and customer engagement. Whereas traditional insurers rely on legacy systems,
InsurTech companies leverage the cloud, AI, IoT, mobile, and APIs to deliver personalized, super-automated insurance experiences. Some even to provide the underwriting & distribution for B2B insurance partners and other brands engaged in embedded insurance experiences.
Understanding Traditional Insurance Models
Customer engagement and retention issue: Legacy insurers rely on agents and call centers for customer engagement but lack adequate, real first-party digital self-service capabilities. A mobile app development company provides an opaque, data-driven, and reactive experience, that drives digitally savvy customers to more engaging and simple InsurTech solutions.
- Reliance on manual processes and legacy systems: Many incumbents still use mainframes, spreadsheets, and manual document filing to issue policies, process endorsements, and handle claims, which leads to errors and longer cycle times.
- Barriers to personalization and a slow time-to-decision: Risk is determined through demographic generalizations and historical averages, leading to the inability to personalize coverage or rates, while approvals and claims can take days or weeks.
- Human underwriters and adjusters: Most underwriting and claims processing costs stem from human underwriters and adjusters, along with siloed data, leading to higher operating costs and lower margins.
- Customer engagement and retention issue: Legacy insurers rely on agents and call centers for customer engagement but lack adequate, real first-party digital self-service capabilities. The resulting experience is opaque, data-driven, and reactive, and drives digitally savvy customers to more engaging, simple InsurTech solutions.
What Makes InsurTech Startups Different?
InsurTech startups differentiate themselves in part by the technology they leverage and by how they think about product development, distribution, and customer value.
- Digital-first mindset – InsurTechs built their processes on the understanding that their customers will use their products through a mobile app, web portal, API, or partner platform, developing an easy, frictionless, and scalable experience.
- Agile product development with speed of innovation – InsurTechs employ agile processes, continuous testing, DevOps, and continuous delivery to iterate quickly using customer feedback and data evolving new coverages, riders, and distribution in weeks and not years—and design customer-centric, simple-to-use, mobile-first insurance products.
- Customer-centric business models – Pricing, coverage, and UX are conceptualized around real-life customer needs, such as on-demand protection, micro-durations, and clear terms.
- Cloud-based architectures with scale – Using a cloud-native stack and modular microservices enables InsurTechs to simply install and scale models to new geographies or business lines while still delivering robust performance and resiliency.
How InsurTech Startups Are Disrupting Traditional Insurance?
The effects of InsurTech disruption can be seen throughout the insurance lifecycle, from onboarding to claims to other processes.
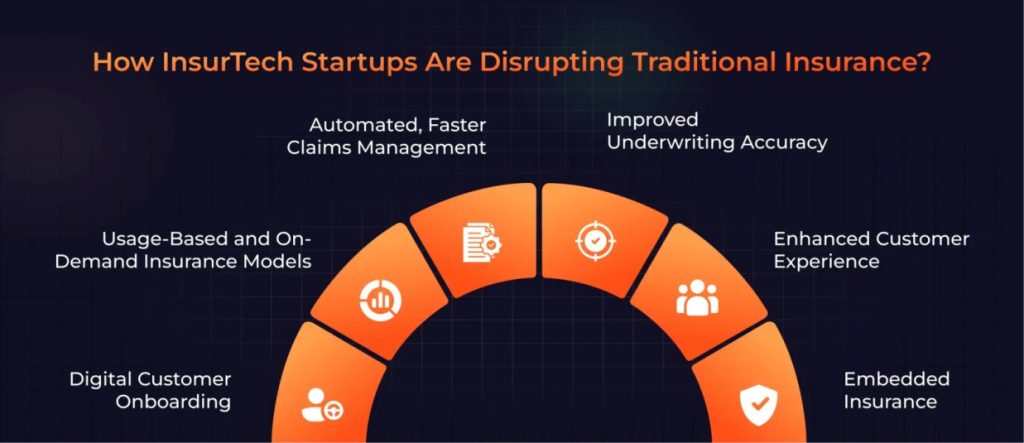
Digital Customer Onboarding
InsurTech companies have replaced branch visits and physical paperwork with seamless digital journeys.
- Fully online enrollment and KYC: Customers can enter their information, authenticate their identity, and fulfill KYC using eKYC, uploaded documents, facial recognition, and third-party checks via secure APIs. Onboarding, which could take days in the past, can now take minutes.
- Instant policy quotes and approvals: AI engines analyze risk in real time, leveraging internal and external data to generate quotes and policy documents within seconds, sometimes without human intervention, resulting in drastically improved conversion rates.
Usage-Based and On-Demand Insurance Models
Static annual policies are being replaced by dynamic, consumption-based insurance.
- Pay-as-you-go auto insurance: Telematics devices or smartphone sensors can monitor driving behavior metrics, such as braking, acceleration, and mileage, allowing insurance premiums to reflect consumer behavior rather than demographic profiles.
- Event-based and microinsurance products: Insurance is available for short periods of time for trips, rides, events, or specific assets. Creation and deactivation processes are initiated within the app, creating greater access and affordability in the purchasing process.
- Pricing customization based on real-time behavior: With auto, property, and health lines, continuous data streams from IoT and wearables enable algorithms to adjust pricing and rewards based on individual risk profiles, most often in conjunction with Health Insurance Software Development platforms.
Automated, Faster Claims Management
Claims processes, often a source of customer frustration, are being simplified dramatically.
- AI-Enabled Claims Submission and Validation: Digital FNOL gives consumers options to report an incident through apps, chatbots, or portals; AI handles the initial case work of validating coverage, collecting data, and facilitating processing, all completely automated.
- Computer Vision to Assess Damage: For auto and property claims, users must upload photos or a video of the property damage; computer vision models can assess the level of damage and repair costs in most cases without a physical inspection.
- Fraud Detection using AI Data Analytics: The machine learning models will flag suspicious behavior, duplicate claims, excessive estimates, and other anomalies, with a focus on reducing fraud losses and speeding up the processing of legitimate fraud claims.
Improved Underwriting Accuracy
InsurTechs are changing underwriting from a static, rule-based process to a modern, data-driven decision-making process.
- Real-time data sources for dynamic risk modeling: Underwriters leverage telematics, health data, geospatial intelligence, and transactional behavior to assemble a more robust risk profile, which provides a better basis for pricing and coverage decisions.
- Minimized human bias and manmade error: Automated scoring in which the algorithm drives decisions minimizes subjective judgment and reduces variability among underwriters, thereby supporting fairness, consistency, and defense against regulatory scrutiny.
Embedded Insurance
Consumers are increasingly purchasing insurance as part of other digital journeys, rather than as an add-on.
- Insurance is sold alongside the point of purchase: InsurTech platforms plug into e-commerce travel, mobility, and financial apps, to enable users to add contextual insurance (i.e. trip insurance, gadget insurance, checkout protection,…) with a single click.
- Willing partnerships with e-commerce, travel, and fintech: APIs, white labeling, and revenue-sharing make it attractive for partners to bundle insurance, making buying insurance feel native and easier while further expanding distribution.
Enhanced Customer Experience
The customer experience is an important area where many InsurTechs differentiate from incumbents. InsurTechs are also building features outside of the core experience as their ecosystem grows and coverage expands, for example:
- Omnichannel support utilizing chatbots and mobile apps: Enterprise chatbots, app-based assistants, and AI-based contact centers answer FAQs (as well as claims status and policy changes) 24/7, ultimately increasing response speed.
- Personalized (policy) recommendations: Based on your lifestyle, transactions, and behavior, data-driven engines suggest the ideal coverage and add-ons vs. the generic marketing segments associated with the incumbents.
- Transparency about policy terms and digital documentation: Clear language, a digital policy “vault” of legal and policy documents, and interactive explanation tools allow customers and prospects to understand what they are covered for, improving trust and reducing disputes.
Challenges Traditional Insurers Face in Competing with InsurTech
Though many incumbents are modernizing, some structural challenges limit their ability to respond effectively to InsurTech disruption.
- Legacy systems limiting flexibility and speed: Core platforms built decades ago are often prohibitively difficult to modify to support a new product launch in a timely way or to integrate real-time data sources or a digital channel.
- Regulatory complexity: Legacy regulated insurers often carry a larger, more complex set of regulatory obligations that often exist across multiple jurisdictions, making rapid experimentation harder.
- Data siloing and limitations with integration: Decentralized IT landscapes, incompatible data model structures, and limited interoperability of APIs all place incumbents further behind in positioning themselves to do analytics and AI broadly as “cloud-native” InsurTechs can focus on further.
- Talent and skills gap: Incumbents seeking to do anything similar must compete with tech companies for contract engineers, product managers, data scientists, and others, which limits the speed and scope of internal transformation.
- Resistance to organizational change: Organizations ingrained in culture, hierarchy, and risk-averse behaviors hesitate to adopt agile, customer-centric behavior even when they have the technology in place.
Final Thoughts
InsurTech startups are not simply layering digital capabilities on top of legacy processes; they are fundamentally restructuring insurance from the ground up, with a sophisticated focus on data, automation, and embedded experiences that complement how people live and transact today.
From instant onboarding and usage-based models to AI-enabled underwriting and claims, they are raising the bar on speed, personalization, and transparency.
Traditional insurers wishing to remain relevant must embrace collaboration and updates, most often through partnerships with providers of Custom Insurance Software Development services to rearchitect their legacy cores, open APIs, and embed analytics across their organizations. Those insurers that are able to leverage their understanding of risk with twenty-first-century technology capabilities will become flexible, customer-obsessed organizations prepared for the InsurTech age.