“Secure user data, enhance business resources, and prevent threats by using AI for cybersecurity.”
Artificial Intelligence is now everywhere! It is in machines, software systems, development tools, and modern innovations, controlling human beings to a limited extent.
The use of AI in cybersecurity and other advanced technologies, such as Blockchain, VR, or IoT, has enhanced the privacy of user data and improved security. Multiple AI cybersecurity systems in different domains, such as healthcare and finance, prevented unethical attacks and security breaches.
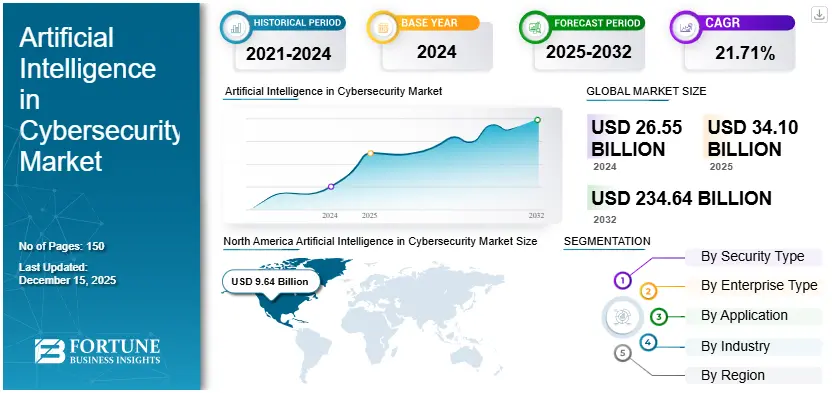
According to a standard cyber firm, the total revenue of AI for cybercrimes till 2025 was $34.1 brillion, which will reach $234.6 brillion by 2032. Investment in money for data security using AI is increasing day-by-day, and not all entrepreneurs can afford it. They can partially implement AI-powered cybersecurity services based on their system requirements.
In this blog, we will study several use cases of AI and cyber that are applicable worldwide. Additionally, a few benefits, major roles, challenges, advanced tools, and future outcomes are also discussed. So, let’s move further to explore more in detail.
Understand the Role of AI in Cybersecurity
At first, it is important to know the role of using AI in cybersecurity, so it is easy to understand the other sections. Let’s discuss some of the crucial AI roles for cybersecurity development:
(a). User Behavior Analysis
Analyzing user activities and overall preferences is the primary role of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity. The development of cybersecurity for AI helps in finding various security threats.
(b). Automated Incident Response
Another role of artificial intelligence in cyber security is to automate responses based on queries or scenarios. It is beneficial to install AI Agents that can generate quick answers to resolve issues.
(c). Predictive Security Intelligence
Some artificial intelligence data security systems can predict security needs and make arrangements. This intelligence is useful in multiple situations, such as generating banking alerts for financial threats.
Key Benefits of AI Cybersecurity Solutions
Several benefits of artificial intelligence in cyber security allow businesses to improve data privacy and authentication. A few of the key advantages are discussed in this section that you must know:
-
Real-Time Threat Detection
Various data threats can be detected easily with real-time artificial intelligence and information security systems. This helps businesses to improve several operations, manage resources, and directly administer user activities.
-
Reduced False Positives
The implementation of AI in cybersecurity enables entrepreneurs to decrease negative results that can impact a large number of users. Additionally, it learns from the unethical data to produce accurate and precise outcomes.
-
Scalable Security Operations
The best AI cybersecurity systems perform business-oriented security operations to manage additional risks with high scalability. With AI and Blockchain, the security of existing systems has improved, preventing the risks of cyber threats.
-
Cost & Resource Optimization
Various AI cybersecurity solutions provide regular maintenance that enhances features and removes system bugs. This operation reduces the overall cost and optimizes services to improve user experiences at affordable rates.
Best Use Cases of AI for Cybersecurity in 2026
Here, key use cases for AI in cybersecurity are described in detail, helping multiple investors in various domains. These industry applications collectively enhance software systems and business processes:

1. AI-Driven Malware Detection
AI-driven malware detection uses machine learning models to analyze files, code patterns, and runtime behavior in real time. It is one of the most widely used AI applications in cybersecurity that identifies known and unknown malware faster than signature-based tools. The use of AI enables proactive threat blocking with minimal false positives.
Business Impact: Reduces breach-related financial losses by identifying and neutralizing advanced malware before execution.
2. Zero-Day Attack Identification
AI identifies zero-day attacks by detecting unusual system behavior, anomalies, and unknown exploit patterns. Instead of relying on predefined signatures, various AI data security systems learn from normal user activities and registered information. This allows security teams to detect previously unseen threats before widespread damage occurs.
Business Impact: Minimizes downtime and reputational damage by detecting unknown threats without relying on signature updates.
3. Phishing Email Detection & Prevention
AI-powered phishing detection methods analyze email content, sender behavior, URLs, and attachments to identify false cybersecurity for AI. In 2026, advanced NLP models detect highly personalized phishing attempts and patterns. The use of AI in mobile apps continuously adapts to evolving social engineering tactics, reducing successful attacks.
Business Impact: Protects revenue and brand trust by preventing credential theft and business email compromise attacks.
4. Ransomware Behavior Analysis
AI monitors file access patterns, encryption activity, and system changes to detect ransomware behavior at early stages. By identifying abnormal file modifications and process execution, artificial intelligence information security systems can stop attacks. This operation is performed before full encryption, minimizing operational disruption and financial loss.
Business Impact: Prevents costly ransom payments and operational shutdowns through early-stage attack detection.
5. User & Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA uses AI to analyze user and device behavior across various networks, applications, and user endpoints. It establishes threshold values for user behavior and flags deviations that indicate compromised accounts or malicious insiders. The implementation of AI in cybersecurity with UEBA enhances threat visibility in complex environments.
Business Impact: Lowers security risk by detecting abnormal user behavior that traditional tools overlook.
6. Automated SOC Operations
Various AI components can automate Security Operations Center (SOC) tasks such as alert generation, incident prioritization, and response workflows. By reducing manual workloads, AI helps SOC teams focus on critical system threats. Businesses are using AI for cybersecurity and SOCs to make operations faster and more efficient in the future.
Business Impact: Cuts operational costs and response time by automating threat triage and incident resolution.
7. Insider Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence detects insider software threats by correlating different access patterns, data usage, and behavioral anomalies. Multiple AI cybersecurity systems can identify both malicious insiders and compromised employee accounts before taking any action. The implementation of AI-driven insights reduces the risk of data breaches caused by internal elements.
Business Impact: Prevents data leaks and IP theft by identifying malicious or negligent internal activity in real time.
8. AI-Based Fraud Prevention
AI-based fraud prevention analyzes transaction behavior, user patterns, and contextual data in real time. It is among the top use cases of Generative AI that help in detecting suspicious activities across banking, e-commerce, and digital payments. Advanced AI-powered cybersecurity models may reduce false positives while improving fraud detection accuracy.
Business Impact: Reduces financial fraud losses by analyzing transactional patterns and stopping fraudulent activity instantly.
9. Cloud Security Posture Management
AI-powered cloud security posture management continuously assesses cloud configurations, permissions, and different compliance risks. It is the best application of AI in cyber security that identifies misconfigurations and policy violations without any extra effort. AI helps organizations maintain secure and compliant cloud environments at every point.
Business Impact: Prevents misconfiguration-driven breaches by continuously assessing cloud compliance and risk exposure.
10. IoT Device Security Monitoring
AI monitors IoT device behavior, network traffic, and communication patterns to detect anomalies with the efficiency of data packets. This is among the best use cases for AI in cybersecurity that identifies compromised or rogue devices at different levels. With expanding IoT ecosystems in various industries, AI ensures visibility and security across connected environments.
Business Impact: Avoids network-wide compromises by detecting and isolating vulnerable or hijacked IoT devices.

11. Vulnerability Prediction
The use of AI in cybersecurity is to predict various system vulnerabilities by analyzing code repositories, system configurations, and historical user data. It helps security teams prioritize software patching based on risk factors, resource allocation, and management. With innovations, predictive AI reduces exposure by addressing weaknesses before exploitation occurs.
Business Impact: Enables proactive patching, reducing exploit risk and saving remediation costs.
12. Threat Intelligence Automation
Several security methods, like threat intelligence collection, correlation, and analysis from multiple sources, are automated by AI. This technology transforms raw data into valuable user insights faster, which is one of the most widely accepted use cases of AI in cybersecurity. These AI-driven threat intelligence methods enable proactive defense against emerging cyber threats.
Business Impact: Improves decision-making speed by converting massive threat data into actionable insights automatically.
13. AI-Powered Endpoint Protection
AI-powered endpoint protection continuously monitors devices for malicious activity and abnormal behavior. The use of AI for Business Process Automation helps in detecting advanced threats such as fileless malware and zero-day exploits. By integrating artificial intelligence in cybersecurity, you can enhance endpoint security with adaptive data protection.
Business Impact: Protects distributed workforces by stopping attacks at the device level in real time.
14. Real-Time DDoS Attack Mitigation
Many DDoS attacks are detected and mitigated by AI, as it analyzes traffic patterns and network behavior in real time. The technology automatically distinguishes malicious traffic from multiple users across the globe. This application ensures service availability during large-scale AI cyber attack attempts without disrupting the overall connectivity of a system.
Business Impact: Ensures service availability and revenue continuity by neutralizing traffic floods instantly.
15. Identity And Access Anomaly Detection
It becomes easy to analyze user login behavior, access requests, and authentication patterns through AI to detect identity anomalies. Businesses can identify compromised credentials, prevent unauthorized access attempts, and enhance data security using AI. This technology strengthens the security of identical operations across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Business Impact: Prevents account takeovers by detecting abnormal login behavior and privilege misuse early.
Essential AI-Powered Cybersecurity Tools
Various AI cybersecurity tools are used in different industries, such as healthcare, finance, and logistics. They track potential risks in the system, create a report, and perform a diagnosis for maintenance:

1. Darktrace
Darktrace uses self-learning AI to detect unusual behavior across networks, clouds, and endpoints in real time. It is one of the best examples of AI in cyber security that autonomously responds to cyber threats before they convert into breaches.
Industry Application: Used in manufacturing plants to detect anomalous network behavior in real time and prevent cyber threats targeting industrial control systems (ICS).
2. CrowdStrike Falcon
CrowdStrike Falcon leverages AI and machine learning to provide cloud-native endpoint protection and threat intelligence. The use of artificial intelligence in cyber security with this tool identifies, prevents, and responds to advanced malware and ransomware attacks.
Industry Application: Protects enterprise endpoints in large IT and industrial environments by using AI-driven threat intelligence to stop ransomware and advanced persistent threats.
3. IBM QRadar with AI
IBM QRadar with advanced AI Frameworks enhances security analytics by correlating huge amounts of data to detect threats faster. Its AI-driven cyber security insights help business teams prioritize and respond to incidents efficiently.
Industry Application: Helps energy and utility companies correlate security events across IT and OT systems to identify and respond to cyberattacks faster.
4. Palo Alto Cortex XDR
Palo Alto Cortex XDR uses AI to unify and analyze data from endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. It reduces alert noise through AI cybersecurity services and enables rapid detection with an automated response for complex attacks.
Industry Application: Enables centralized threat detection and automated response across industrial networks by analyzing data from endpoints, networks, and cloud systems.
5. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint applies AI-driven threat protection to detect, investigate, and prevent potential endpoint risks. It seamlessly integrates AI data security with Microsoft security tools for proactive cyber defense.
Industry Application: Secures industrial enterprise devices by detecting, investigating, and mitigating endpoint-based cyber threats using AI-driven analytics.
Challenges of Integrating AI in Cyber Security Systems
There are multiple challenges associated with the process of integrating AI in cybersecurity systems. In this section, we are going to observe key technical issues with their respective solutions:
1. Data Quality & Bias
Most digital systems reduce data quality due to limited software services and processes. There is a conflict in developing AI-based cybersecurity systems, as the structure is complex and unique.
Solution: Perform model analysis to identify business needs and ensure standard data quality.
2. High Implementation Costs
The AI Agent development cost is high because it requires the latest algorithms that can automate security. Using AI agents in cybersecurity may influence the business model with increasing expenses.
Solution: Target cost-effective and effective AI solutions for the security of software systems.
3. Adversarial AI Attacks
The integration of cybersecurity and AI does not completely ensure data protection and the prevention of bidirectional attacks. Low-code AI algorithms may lead to security threats and data loopholes.
Solution: Use advanced AI models to handle complex operations and reduce possible data risks.
What is the Future of AI for Cyber Security?
In the future, more innovations are expected for AI in cybersecurity because of increasing demand. Different futuristic trends are discussed in this section that are crucial to know:
1. Autonomous Security Operations
AI used in cyber security can detect, investigate, and respond to cyber threats without human intervention. This will significantly reduce response times and minimize damages caused by complex security attacks.
2. Predictive Cyber Defense
Businesses using AI in cyber security can analyze historical data and threat patterns to predict cyberattacks. The AI for Enterprise helps in strengthening systems and preventing breaches in advance.
3. AI vs AI Cyber Warfare
In the future, attackers will use AI-driven malware while defenders deploy AI cybersecurity systems. This ongoing battle will accelerate the evolution of both offensive and defensive cyber technologies.
4. Hyper-Personalized Security Controls
AI and data security will guide security measures based on user behavior, roles, and risk profiles. This personalization will enhance protection while reducing friction and false alerts for legitimate users.

Let’s Summarize!!
Now, we have arrived at a point where everything is crystal clear about the use of AI in cybersecurity to protect sensitive information from malicious attacks.
The integration of AI and cybersecurity helps entrepreneurs to improve business operations, enhance security, and encourage fraud detection. It is beneficial to use AI development services that can implement automated algorithms and predictive maintenance for software systems.
Businesses should target multiple applications of artificial intelligence in cyber security that cover customer support, attack prevention, and malware analysis.
Additionally, they can develop advanced AI data security systems for tracking data packets and converting them into usable formats. This will improve the overall efficiency and productivity that most entrepreneurs target.
FAQs
To ensure the security of user data and business resources, it is crucial to know how to develop AI-powered cybersecurity platforms. The key development steps are discussed as follows:
- Define security objectives and threat models to identify risks AI should detect and prevent.
- Collect and preprocess large volumes of high-quality security and network data.
- Train machine learning models to detect anomalies, malware, and cyberattack patterns.
- Integrate AI models with existing security tools for real-time monitoring and response.
- Continuously test, update, and improve models to adapt to evolving cyber threats.
Yes, artificial intelligence in cybersecurity systems can easily predict various threats and attacks that can occur in the future. It runs an algorithm to analyze all possible backdoors and open channels that lead to security breaches. Additionally, AI helps in identifying bugs and viruses that force the system to produce inaccurate results, which may lead to data fraud.
Generative AI helps to mitigate risks, predict potential security attacks, analyze reports, and enhance fraud detection models. Additionally, it generates quick responses and improves the overall security infrastructure. It provides multiple security instructions based on performance analysis and optimizes the complete architecture before damage.
Advanced cybersecurity solutions with artificial intelligence have a large impact on most industries. The key factors are discussed in the following manner:
- Detects and prevents cyber threats in real time with minimal human intervention.
- Reduces financial losses by predicting, identifying, and mitigating attacks faster.
- Enhances compliance, data protection, and overall digital trust across industries.
AI has multiple components that are used to enhance cybersecurity services and improve fraud detection. Some of the major contributors are described as follows:
- Machine Learning: The algorithms analyze patterns to identify anomalies and threats.
- Natural Language Processing: It helps detect phishing, spam, and social engineering attacks.
- Predictive analytics: This monitors user and system behavior to spot suspicious activity.









